Attention: The Origin of Transformer
Paper: Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate
This paper (Bahdanau et al., 2014) introduced attention for sequence-to-sequence models. The idea later became the core mechanism behind Transformers.
Why attention
Classic encoder-decoder RNNs compress the entire source sequence into a single fixed-length vector. For long sentences, that vector becomes a bottleneck. Attention replaces the single vector with a dynamic context that changes at every decoding step.
Alignment weights
At decoding step \(i\), the model assigns a weight to each encoder state \(h_j\): \[ a_{ij} = \frac{\exp(e_{ij})}{\sum_{k=1}^{T_x} \exp(e_{ik})}, \] where \(T_x\) is the source length. The weights are positive and sum to 1.
The attention score
The alignment score compares the previous decoder state with each encoder state: \[ e_{ij} = a(s_{i-1}, h_j). \] A common formulation in the paper is additive attention: \[ e_{ij} = v^T \tanh(W_s s_{i-1} + W_h h_j). \]
- \(s_{i-1}\): decoder hidden state from the previous step
- \(h_j\): encoder hidden state for source position \(j\)
- \(W_s, W_h\): projections into a shared attention space
- \(v\): learned vector that converts the hidden interaction into a scalar score
This is conceptually similar to Transformer query/key projections, but with an additive scoring function instead of a dot product.
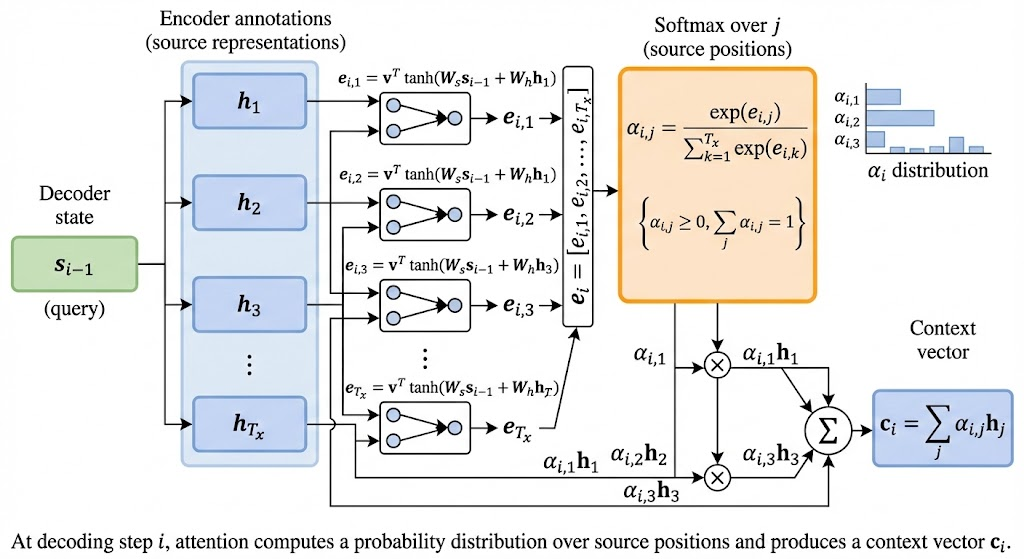
The context vector
The context vector is a weighted sum of encoder states: \[ c_i = \sum_{j=1}^{T_x} a_{ij} h_j. \] This lets the decoder focus on different parts of the input as it generates each token.
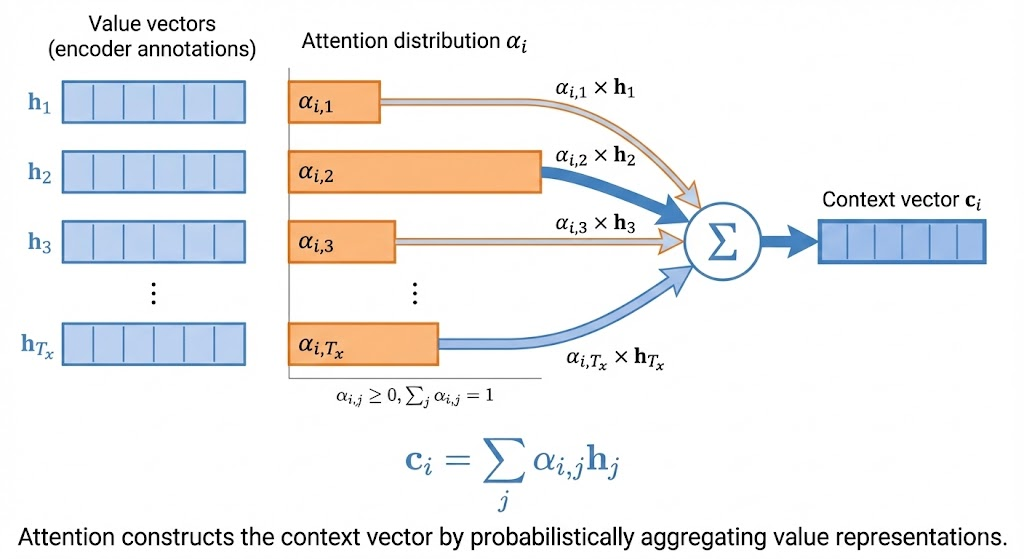
Connection to Transformers
- Queries: decoder state \(s_{i-1}\)
- Keys/Values: encoder states \(h_j\)
- Weighted sum: context vector \(c_i\)
Transformers generalize this idea with multi-head attention and parallel computation, but the core intuition is the same: soft alignment over the source sequence.
Takeaway. Attention removes the fixed-vector bottleneck by letting the model compute a new context at every step. That single change enabled far better long-sequence modeling and inspired the Transformer architecture.