Goodfellow Deep Learning — Chapter 10.3: Bidirectional RNN
In some applications, the prediction of \(y^t\) may rely on the entire input sequence, not only \(y_1,...y^{t-1}\). For example, in speech recognition, correctly interpreting the current sound often depends on acoustic cues that appear later in the sequence.
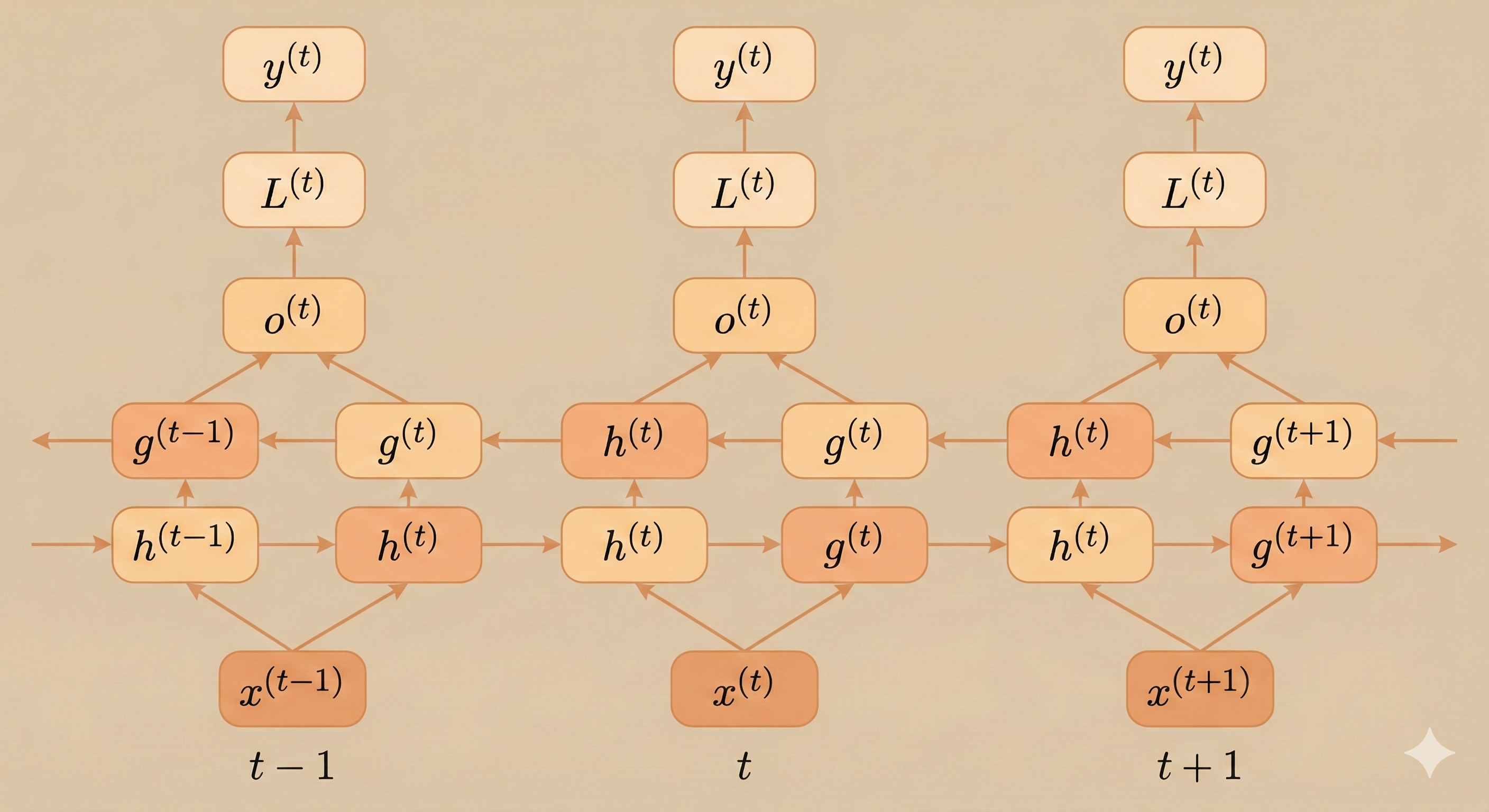
Bidirectional RNNs were designed specifically to address such cases.
By incorporating information from both past and future inputs, they have achieved great success in inherently bidirectional tasks such as handwritten text recognition, speech recognition, and biological sequence analysis.
Architecture
Obviously, a bidirectional RNN combines two RNNs: one that processes the sequence from the beginning to the end, and another that runs in the reverse direction.
This allows the output unit \(o^{(t)}\) to receive information from both the past and the future.
Bidirectional RNNs can also be extended to operate on 2-D structured inputs, such as images, where four directional RNNs (left, right, up, and down) may be used to capture context in all spatial directions.