Goodfellow Deep Learning — Chapter 7.7: Multi-Task Learning
Overview
Multi-task learning trains a single model to perform multiple related tasks simultaneously by sharing representations across tasks. This approach:
- Improves generalization by learning shared features
- Reduces overfitting through implicit regularization
- Enables knowledge transfer between related tasks
1. Concept
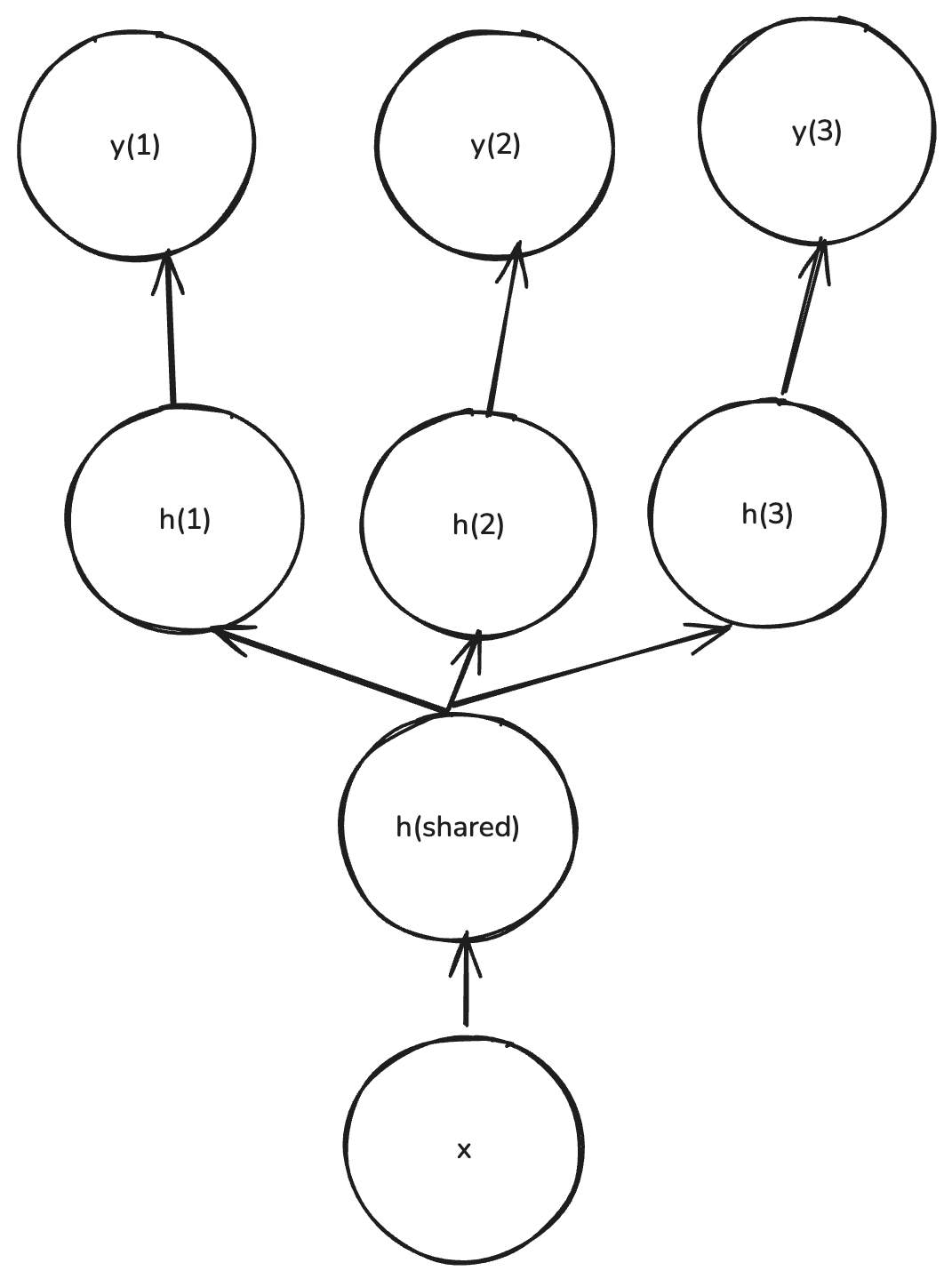
Model Architecture
Multi-task learning uses a shared representation with task-specific outputs:
Training: \[ \begin{aligned} h &= f(x; \theta_{\text{shared}}) \\ \hat{y}^{(t)} &= g(h; \theta_t) \end{aligned} \]
where:
- \(h\): Shared representation (common features learned across all tasks)
- \(f(x; \theta_{\text{shared}})\): Shared layers (e.g., CNN encoder, Transformer)
- \(g(h; \theta_t)\): Task-specific head for task \(t\)
- \(\theta_{\text{shared}}\): Shared parameters
- \(\theta_t\): Task-specific parameters
Loss Function
Combined loss: \[ \mathcal{L} = \sum_t \lambda_t \mathcal{L}_t(g(f(x; \theta_{\text{shared}}); \theta_t)) \]
where:
- \(\mathcal{L}_t\): Loss function for task \(t\)
- \(\lambda_t\): Weight for task \(t\) (controls importance)
- Sum is over all tasks
Interpretation: The model minimizes a weighted combination of task-specific losses, forcing the shared representation to be useful for all tasks.
2. Benefit
Multi-task learning improves generalization ability and reduces generalization error.
Why this works:
- Shared representations: Common features learned from multiple tasks are more robust and general
- Implicit regularization: Training on multiple tasks prevents overfitting to any single task
- Data efficiency: Each task benefits from the data of other tasks
- Inductive bias: The model is encouraged to learn features that are useful across tasks
Example:
- Training on both face recognition and age estimation helps the model learn better facial features than training on either task alone
- The shared features capture general facial characteristics useful for both tasks
3. Limitation
Multi-task learning works only when the assumption that the tasks are related statistically holds.
When it fails:
- Unrelated tasks: If tasks are not related, sharing representations can hurt performance
- Negative transfer: A poorly performing task can degrade the shared representation
- Task interference: Conflicting objectives can prevent convergence
Examples of unrelated tasks:
- Face recognition + financial fraud detection (no shared structure)
- Medical diagnosis + game playing (different domains entirely)
Key principle: Tasks should share some underlying structure or statistical properties for multi-task learning to be beneficial.
4. Real-World Cases
Note: The following table is generated by ChatGPT.
| Domain | Tasks Learned Together | Shared Representation / Model | Practical Benefit | Example / Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Face Analysis | Face recognition · Age estimation · Gender / Emotion classification | Shared CNN backbone (e.g., ResNet) with multiple output heads | Improves accuracy and robustness by using shared facial features | Zhang et al., MTL-CNN for Face Analysis, CVPR 2014 |
| Autonomous Driving | Object detection · Lane segmentation · Depth estimation | Shared encoder in perception network | Enables one network to handle multiple perception tasks → reduced compute & latency | Uber ATG, MultiNet, CVPR 2017 |
| Medical Imaging | Tumor segmentation · Disease classification | Shared U-Net encoder with task-specific decoders | Combines fine-grained segmentation and diagnosis → less labeled data needed | Liu et al., MT-UNet, MICCAI 2019 |
| Speech Processing | Phoneme recognition · Speaker ID · Emotion detection | Shared acoustic encoder (e.g., wav2vec backbone) | Improves noise robustness and transfer learning across tasks | Baevski et al., wav2vec 2.0, 2020 |
| Natural Language Processing | POS tagging · NER · Parsing · Sentiment analysis | Shared Transformer encoder (e.g., BERT) with task-specific heads | Learns richer linguistic features; boosts low-data tasks | Collobert et al., Unified NLP with MTL, 2008; Devlin et al., BERT, 2019 |
| Search & Recommendation | Click prediction · Conversion rate · Dwell-time estimation | Shared user-embedding network | Captures user intent across tasks → higher CTR and ranking precision | Google Ads / YouTube Recommender Systems |
| Financial Risk Modeling | Credit default · Fraud detection · Customer churn | Shared behavior-feature extractor | Reduces training cost, improves detection of rare events | Ant Financial Research Team, 2020 |
| Robotics / Reinforcement Learning | Navigation · Object manipulation · Balance control | Shared policy network or shared latent state | Learns transferable motor skills across tasks | DeepMind IMPALA (2018), Gato (2022) |
Source: Deep Learning Book (Goodfellow et al.), Chapter 7.7