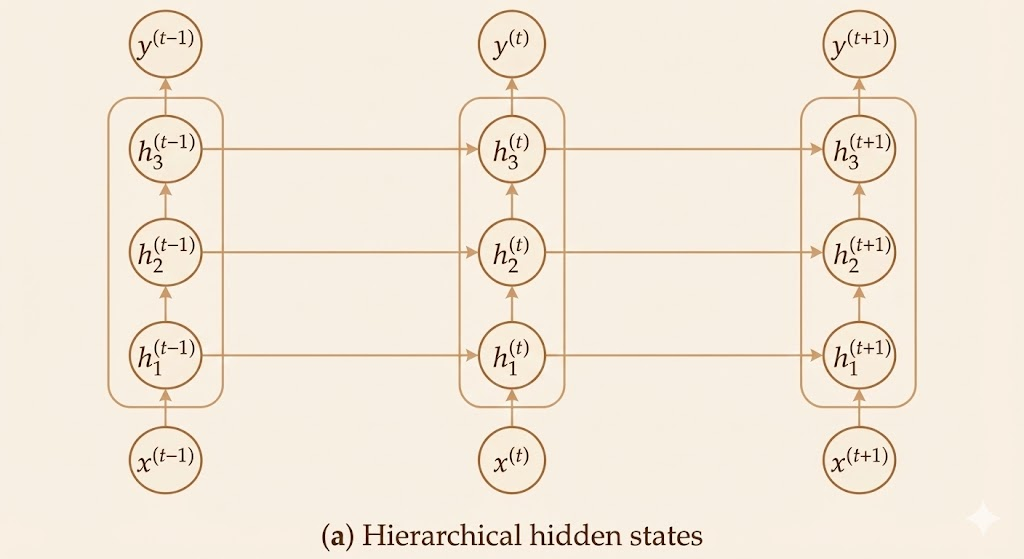
Goodfellow Deep Learning — Chapter 10.5: Deep Recurrent Networks
Deep recurrent networks extend basic RNNs by introducing depth through multiple layers of computation. The experimental literature on deep RNNs emphasizes three main architectural patterns for adding depth:
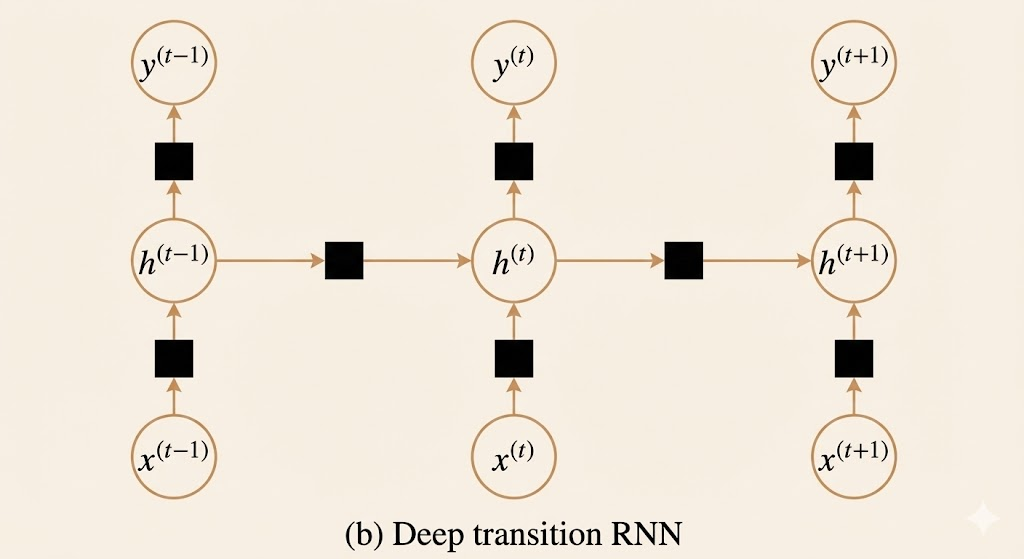
2. Deep Transition RNN
Instead of using simple affine transformations followed by activation functions, the core RNN transformations are replaced by multilayer perceptrons (MLPs).
The three key transformations become:
- Input-to-hidden: \(\text{MLP}_x(x_t)\)
- Hidden-to-hidden (recurrent): \(\text{MLP}_h(h_{t-1})\)
- Hidden-to-output: \(\text{MLP}_o(h_t)\)
Each MLP is a small feedforward network with its own hidden layers, adding depth within each time step.
Key benefit: Richer transformations at each step—capable of learning more complex nonlinear mappings between successive hidden states.
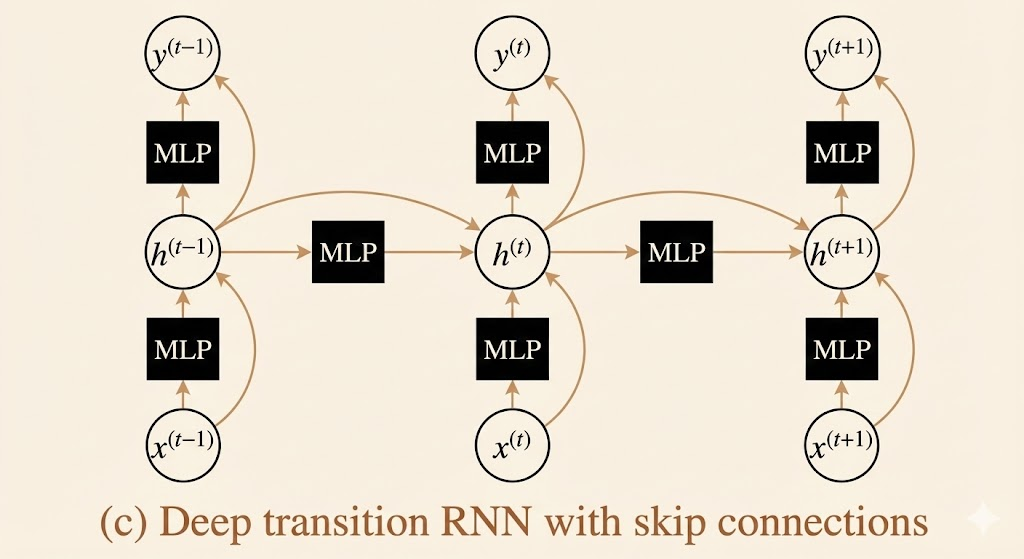
3. Deep Transition RNN with Skip Connections
This architecture extends the deep transition RNN by adding skip connections (residual connections) around the deep MLP blocks.
At each time step, the input to an MLP is added directly to its output:
\[ h_t = \text{MLP}_h(h_{t-1}) + h_{t-1} \]
This follows the residual learning principle popularized by ResNets.
Key benefit: Skip connections enable gradient flow through very deep networks by providing shortcut paths that bypass multiple nonlinear transformations. This mitigates vanishing gradients and allows training of much deeper RNN architectures.
Comparison and Trade-offs
| Architecture | Depth Location | Parameters | Gradient Flow | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical | Vertical stacking | High | Standard BPTT | Multi-scale temporal patterns |
| Deep Transition | Within transformations | Very high | Challenging | Complex state transitions |
| Deep Transition + Skip | Within transformations | Very high | Improved | Very deep networks |
General principle: Adding depth to RNNs increases expressiveness but also increases the risk of optimization difficulties. Skip connections are essential for training very deep recurrent architectures.
These three patterns can be combined—e.g., hierarchical RNNs where each layer uses deep transitions with skip connections—to build highly expressive sequence models at the cost of increased computational requirements.