Goodfellow Deep Learning — Chapter 10.10: LSTM and GRU
Deep Learning Book - Chapter 10.10 (page 400)
Like leaky units, LSTM mitigates vanishing and exploding gradients by introducing explicit memory paths through time, but does so adaptively via learned gates rather than fixed time constants.
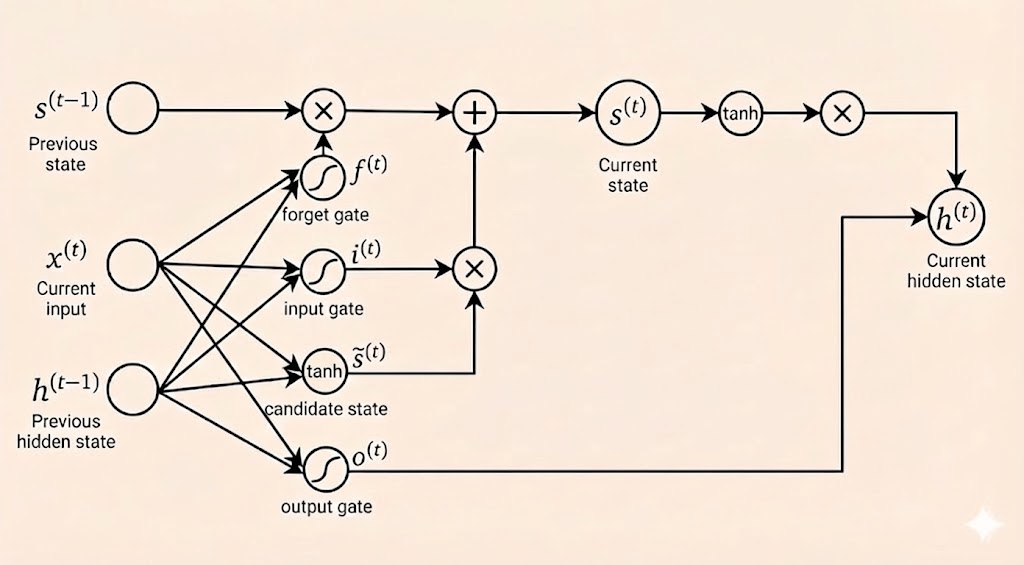
LSTM
The Gates
forget gate (\(f\)) The forget gate controls how much of the previous cell state \(s^{(t-1)}\) is retained, enabling the model to selectively preserve long-term information.
\[f^t=\sigma(W_fX^t+U_fh^{t-1}+b_f)\]
input gate (\(i\)) The input gate determines how much newly computed candidate state \(\tilde{s}^{(t)}\) should be written into the cell state.
\[i^t=\sigma(W_iX^t+U_ih^{t-1}+b_i)\]
candidate state (\(\tilde{s}\)) The candidate state represents the new information to be added to the cell state.
\[\tilde{s}^t=\mathrm{tanh}(W_cX^t+U_ch^{t-1}+b_c)\]
output gate (\(o\)) The output gate controls how much of the internal cell state is exposed as the hidden state \(h^{(t)}\).
\[o^t=\sigma(W_oX^t+U_oh^{t-1}+b_o)\]
Cell State
The cell state combines the previous state (gated by forget gate) with new candidate information (gated by input gate):
\[s^{(t)} = f^{(t)} \odot s^{(t-1)} + i^{(t)} \odot \tilde{s}^{(t)}\]
GRU
The Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) simplifies the LSTM by merging the forget and input mechanisms into a single update gate, which jointly controls how much past state is retained and how much new information is incorporated.
The Gates
update gate (\(z\)) The update gate controls how much of the previous hidden state is retained versus replaced with new information.
\[z^{(t)} = \sigma(W_z x^{(t)} + U_z h^{(t-1)} + b_z)\]
reset gate (\(r\)) The reset gate controls how much of the previous hidden state is used when computing the candidate hidden state, allowing the model to ignore past information when needed.
\[r^{(t)} = \sigma(W_r x^{(t)} + U_r h^{(t-1)} + b_r)\]
hidden state (\(h\))
candidate hidden state The candidate hidden state represents newly computed information based on the current input and a gated version of the previous hidden state.
\[\tilde{h}^{(t)} = \tanh(W x^{(t)} + U (r^{(t)} \odot h^{(t-1)}) )\]
final hidden state The final hidden state is a weighted combination of the previous state and the candidate state.
\[h^{(t)} = (1 - z^{(t)}) \odot h^{(t-1)} + z^{(t)} \odot \tilde{h}^{(t)}\]
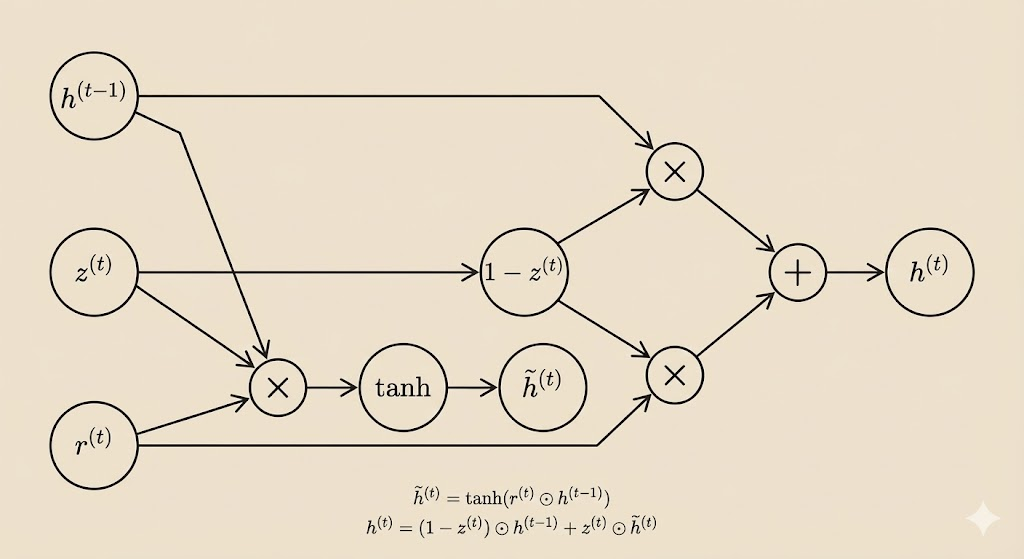
This diagram shows the core GRU recurrence, omitting affine input terms for clarity